Tags | |
UUID | 19fc3961-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
Nernst Equation
|
The Nernst Equation enables one to determine electromotive forces (emf) of many processes, for instance the resting potential of cell membranes. We can then deduce the biological standard potentials which are important in studying biological process such as action potential during a spike of a neuron in response to a stimulus. Introduction
The Nernst Equation is derived from the emf and the Gibbs energy under non-standard conditions.
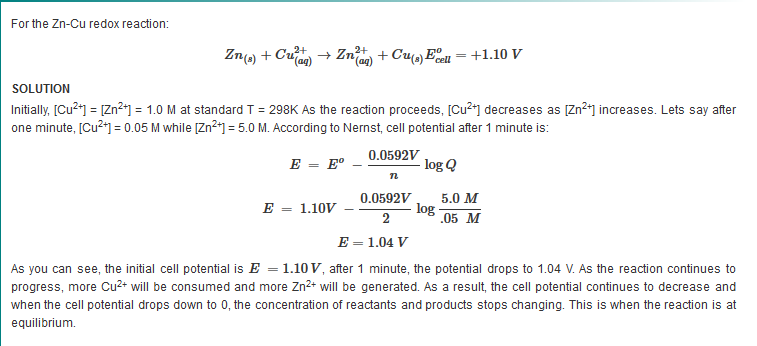
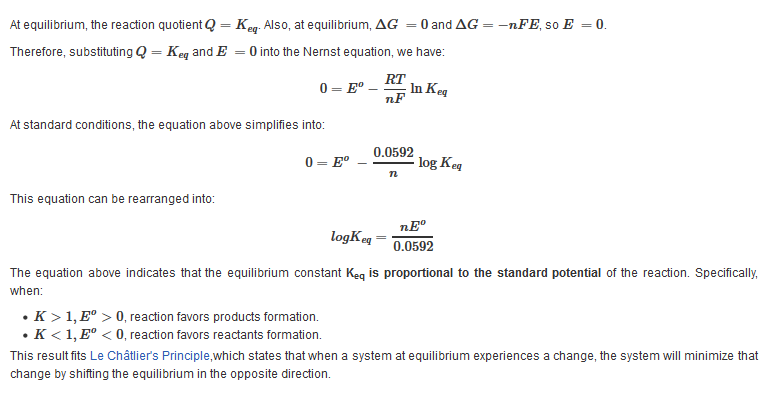
The equation above indicates that the electrical potential of a cell depends upon the reaction quotient Q of the reaction. As the redox reaction proceeds, reactants are consumed, thus concentration of reactants decreases. Conversely, the products concentration increases due to the increased in products formation. As this happens, cell potential gradually decreases until the reaction is at equilibrium, at which ?G =0.
|
||||||||||||||
This Collection is empty
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |